Brain Science Principles Underlying Flow Immersive
Flow Immersive leverages key principles of cognitive neuroscience to make data visualization more engaging, memorable, and effective. These principles span multiple brain systems that process perception, memory, and motivation.

How did we tune Flow to overcome the brain science failures of PowerPoint?? Below is an overview of the main concepts:
1. Visual Processing and the Occipital Lobe
3D Visual processing:
- The occipital lobe, located at the back of the brain, is the primary visual processing center. When users see data in three dimensions—rotating, scaling, and relating objects in space—the occipital lobe works intensively to:
- Identify objects (e.g., recognizing a cube regardless of angle).
- Perceive spatial relationships.
- Detect motion and texture.
- Rich 3D visualization creates deeper neural activation compared to flat images or video. This enhances comprehension of structure and relationships within data.
2. Spatial Awareness and the Hippocampus
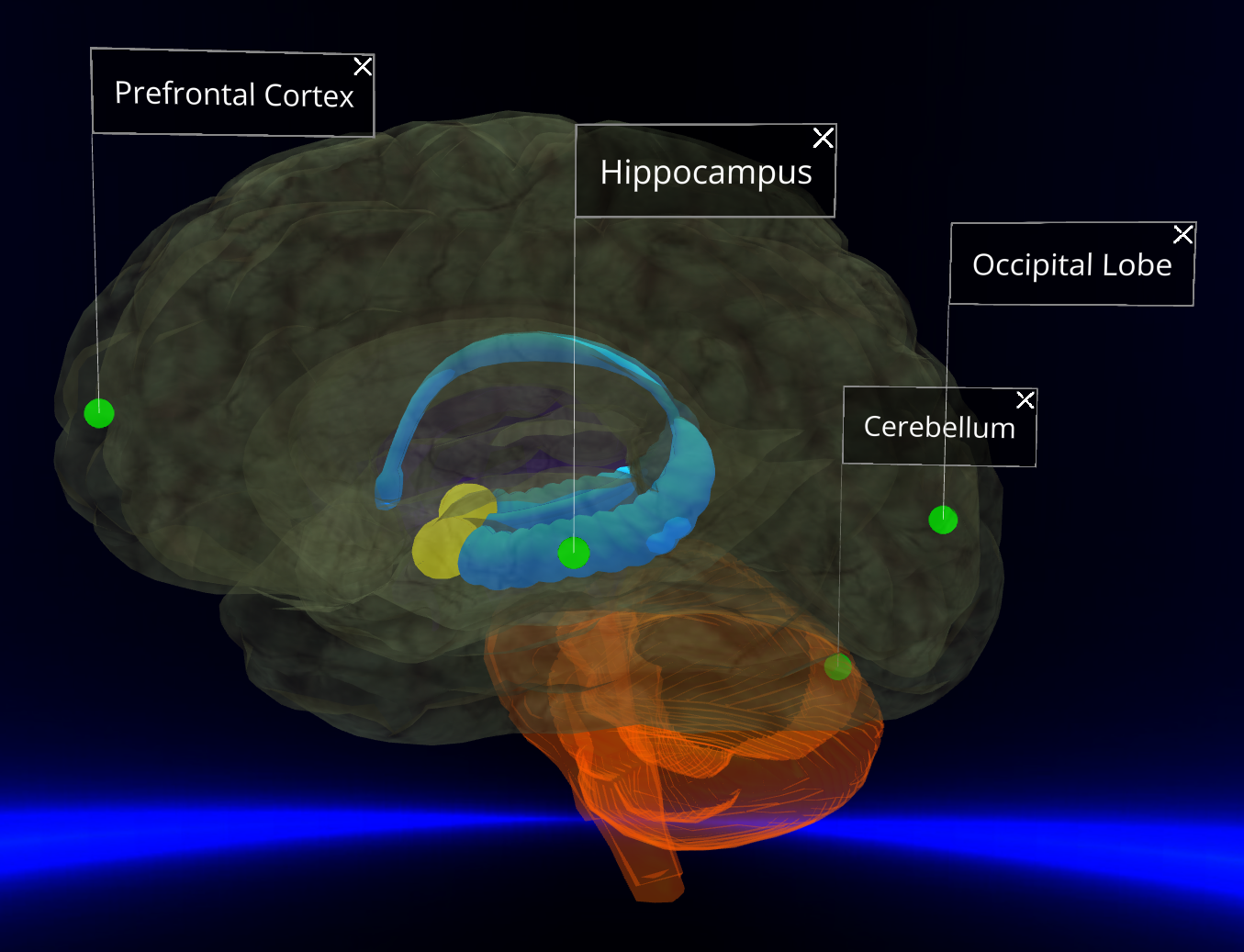
Spatial Encoding:
- The hippocampus plays a dual role in spatial awareness and memory formation. This ancient part of the mammalian brain evolved to help organisms map their environment (e.g., where exits are in a new building).
- By situating data spatially around the user, Flow taps into this system. The hippocampus creates a “mental map” of where information was encountered in virtual space.
- People often recall not just the content but where it appeared in the room, strengthening retrieval cues. This is why users frequently remember Flow visualizations years later - something almost never reported with traditional slides.
3. Meaning-Making and the Prefrontal Cortex
Interpretation:
- The prefrontal cortex assigns meaning to sensory input and helps users decide what is relevant and how to act on it.
- Interactivity (e.g., asking to show Germany’s data) requires active decision-making, reinforcing understanding and personal relevance.
4. Neuroplasticity
Brain Adaptation:
- When experiences are novel, rich, and interactive, they stimulate neuroplasticity - the brain’s ability to reorganize connections. This is relevant for revealing new concepts and building new neural pathways that change minds.
5. Mastery & Control, Prediction
Mastery & Control:
- Flow emphasizes giving users a sense of control - being able to manipulate, explore, and direct the visualization themselves. This feeling of mastery is inherently motivating and often associated with the experience of something “cool.”
6. Animation and Prediction
Predictive Satisfaction:
- The brain rewards prediction that is satisfied. Animations in Flow (e.g., ripple sequences) let users see data assembling in ways that match expectations, producing small dopamine rewards and a sense of satisfaction.
7. Interactivity and Personal Relevance
Active Engagement:
- Interactivity ensures learners are not passive observers. When users direct the visualization themselves (“Show me X”), they create stronger connections and more durable memories.
Summary of Cognitive Benefits
Flow Immersive integrates these elements to optimize:
- Activation of the occipital lobe for rich visual understanding.
- Encoding into spatial memory via the hippocampus.
- Meaning-making in the prefrontal cortex.
- Motivation through mastery
- Predictive satisfaction.
- Neuroplastic adaptation through active participation.
These combined factors make Flow more effective than conventional 2D presentations and more likely to result in deep, durable learning.
Next Steps
I would love to collaborate with neuroscientists to further validate (or in-validate!) and refine these explanations, especially regarding:
- The specific role of hippocampal spatial encoding.
- Long-term retention mechanisms in 3D immersive learning.
- The impact of prediction and mastery on dopamine pathways.


